Coronavirus: Impact on Global Economy
The spread of Covid-19 pandemic was ever faster than the world could imagine. The alarming speed infected millions, carrying the world economies to a standstill, causing largest of the economic shocks that the world ever saw.
The recession during this time was deepest across the globe and developing countries faced irreparable vulnerabilities. The focus shifted to public health systems and not much of the work of governments could be diverted to growth. Each country was engaged in countering the impacts that the coronavirus brought with it.
Also Read: The Impact of Covid-19 on the Economy of India
But by the end of March 2021, there were no winning economies but there were only fewer losers in global economies. The world was on a recovery path by the third quarter of 2020 as the restrictions lifted.
But, the second wave of virus came to Western Europe earlier than expected during final quarter of 2020; it hit India hard by the end of first quarter of 2021, devastating the lives of people from around the country.
In other parts, the pressures went down due to the vaccine breakthroughs and better lockdown measures. Although the world is on the way back to normal they are counting the costs.
Here is an overview of how coronavirus impacted each section of economic activity.

Global Shares Fluctuated
Stock Markets saw very big shifts and affected the value of individual savings accounts. Dow Jones, and the Nikkei,all saw huge falls while the covid was on rise after March 2020. By the year 2021 Asian and US stock markets recovered.
Central banks slashed interest rates to make borrowing cheaper, easy and revive the weakening markets. By the months April and May of 2021 set in, the negative impact of the outbreak gradually fell to taper off, only with the exception of a few countries like India and Taiwan. Asian markets were the ones affected the most during one year of pandemic.
Jobs Lost
An innumerable number of people lost jobs or saw income cuts during the pandemic as the companies struggled to cope up with the downsizing market demands.
- Unemployment rates went up even in financially well countries like America.
- In the United States, the proportion of people out of work reached 8.9%. This indicated an end to the job expansion opportunities not just in America, but all over the world.
- Tourism and Hospitality came to a halt suddenly and have not opened up yet.
- New job opportunities are also too low in many developed countries like France, Spain, and UK, etc.
According to ILO, “there was an extraordinary global employment loss in 2020 of 114 million jobs relative to 2019”.
Related Article: Unemployment in India due to Coronavirus
Countries in Recession
Although IMF predicted global growth of @5.2% in 2021, the only economy that grew was China, by 2.3%. The last year had harmed the poor and vulnerable to the maximum, and millions were pushed to poverty. The restrictions triggered a global crisis leading to the deepest global recession from the times of the Second World War.
Micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) of the countries came under intense pressure. Millions were left without meals, households were compelled to take harsh decisions on household spendings, lives and livelihoods were upset. While the virus is here to stay, effective treatments and vaccinations will facilitate transitions of post-pandemic economy
Travel and Tourism Industry Crumbled
The travel industry was completely devastated due to pandemic. Business trips, holidays, and travel decisions were canceled by customers. Tighter restrictions during travel lead to a huge hit on the number of flights globally, and there is still not much of hope for recovery in this year.
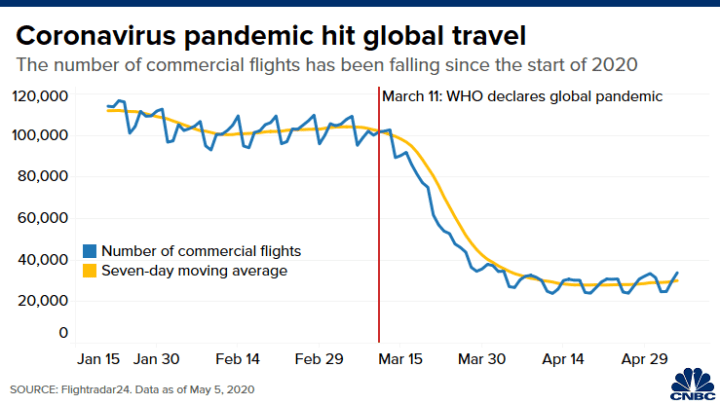
Hospitality also remained shut for a very long period, with millions of jobs lost and companies going bankrupt. The forecast for 2021 was better, but by this time millions of dollars were lost. Travel and hospitality will take a long time to return to the normal pre-pandemic levels.
Retail Footfalls Were Lowest
As the shoppers stayed at home, people preferred shopping online. Online shopping grew large in numbers. Bit brick and mortar, grocery shops, malls and retail stores did not see footfalls. Online market grew drastically, and there was a new baseline for e-commerce sales which will grow beyond expectations from here on.
The high street went in pressure calling for store closures. In near future government will have to take measures for the reinvention of high street in future. Research suggests that consumers will not be willing to visit stores any sooner, so companies are anxious about returning to the store model. Not many of the customers are willing to travel for shopping.
Pharmaceutical Companies among the Winners
Billions of dollars are pledged on Covid-19 vaccine and treatment-related companies. Shares of some vaccine developing companies like Moderna, Novavax, and AstraZeneca shot up. The stringent lockdowns of April and May in 2020 lead to a steep 11% slump in drug sales.
Worst was the condition of anti-infectives and other acute segments because the visits to clinics and out-patient departments of hospitals shrank. In 2021, however, the pharmaceutical industry was prepared for the production and distribution of important drugs to battle the second wave of the pandemic.
As 2021 set in this became a winning industry as the vaccine doses were being distributed by this time and demand for other drugs also increased shooting up the sales.
Economic Recovery Programmes and Rebounding Economies
All the nations and their governance mechanisms worldwide announced programmes for economic recovery. The global economic recovery began in the third quarter of 2021.
The countries began lifting restrictions. This was mainly due to vaccine breakthroughs and improved lockdown measures. 65% of the globe’s manufacturing and exports were hardest hit.
A lot of policies emphasized healthcare equipment, personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilators, and more. Panic buying increased due to the uncertainties. The supply chain was disrupted badly and the question of whether the supply chains will return to normal in recent times to come?
- For global manufacturing, there was a swift recovery from the pandemic and is set to grow in the year 2021. Hi-tech goods, household goods, and pharmaceuticals grew at fastest pace.
- The Speed of recovery is uncertain. Globally the economies contracted by 3.6% in 2020 and there is a forecast of rebound rate at 5.3% in 2021. However, more infectious and spreads in upcoming waves may lead to more intense restrictions again.
- China was the first to recuperate from this pandemic. Business activities resumed there and the country saw a robust v-shaped recovery. They returned fully to pre-pandemic levels by quarter 3 of 2020.
- One year from the outbreak of the virus, Middle East also returned from lockdown but was not into the earlier state yet. The malls opened but footfall was less and many local and regional players shifted to local production for sufficient supplies within the country.
- In Brazil, political instabilities were the worst and economic prospects were dim. Despite the pessimism, the expectations from alcoholic drinks, packaged food, home, garden, and consumer electronics industries were at a high. But the food service and travel sectors kept struggling to overcome social distancing measures.
- Worldwide the consumer expenditure fell and hotels, catering, and transport felt biggest declines. To pent up demands there is an increasingly desperate need to socialize again.
- Ecommerce became a lifeline during these hard-hit times. E-commerce industry posted a 26% growth in the year when other industries struggled to cope with the going changes and found survival difficult.
- Travel and tourism continue to face challenges bearing a devastating impact. Tourism spending in the world collapsed by a big 57% in 2020. The uncertainty still prevails but the growth may speed up with the scale of mass vaccinations.
- There was an extreme impact to business operations in terms of restricted travel and mandatory working from home for employees. Looking at long-term effects, working from home is expected to become a permanent feature of life after a pandemic.
- The world stands intensively polarized after the pandemic hit. Resurfacing lockdowns, restricted borders, digital encroachment, employment inactivity have increased more than ever, according to ILO. Business insolvencies in region and the increasing gap between rich and poor have left the world politicized and polarized.
On a positive note, businesses can use this opportunity to build back. With the paradigm shifts in consumer expectations, businesses can do much better by tackling global issues. There is activism as brands are also taking social actions. Businesses now talk about purpose and responsibility rather than sustainability. This trend is not going to fade away any sooner.
Also Read: